ENGINE REPAIR
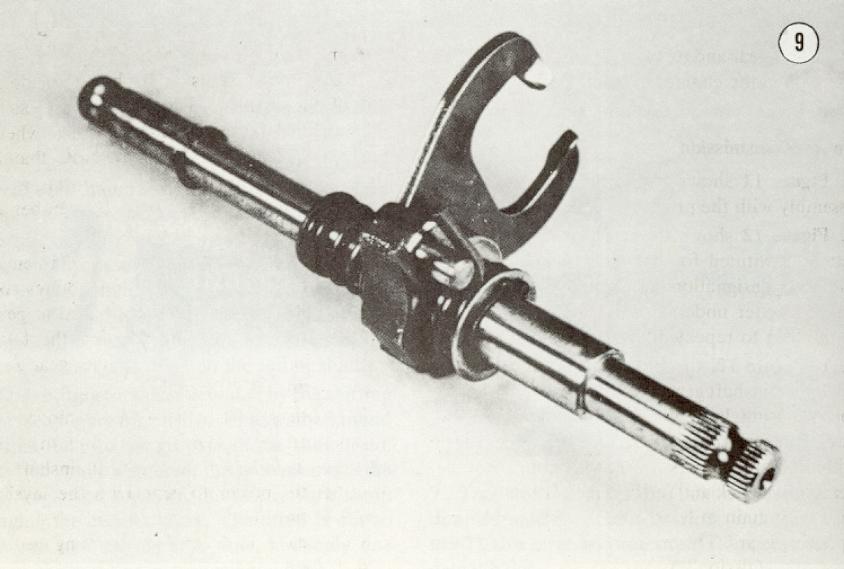
11. The shifting drum is turned by the selector shaft
assembly (see Figure 9). The foot shift lever is fastened to the
selector shaft. The shaft passes all the way through the engine,
so the foot shift lever can be fastened on either end.
12. The selector shaft assembly contains the selector shaft, a spring
loaded selector pawl, a selector return spring, and the foot shift lever.
13. When the foot shift lever is moved, the selector shaft rotates
and the selector pawl engage ' s one of the selector pins on the end of
the shift drum. This turns the drum to the next gear position.
14. When the foot shift lever is released, the selector spring brings
the selector shaft back to its original position. The spring loaded
selector pawl snaps over the top of the next selector pin on the shift
drum, ready for the next gear change.
15. The selector shaft assembly can only turn the shift drum enough
to engage the next closest gear, up or down, to the present gear.
16. The kick starter assembly (see Figure 10) operates through the
main shaft of the transmission. This assembly contains the kick starter
shaft, a spring loaded ratchet cam, a driving gear, a return spring, a
foot lever, and a stop bolt, which is threaded into the right engine case.
17. The ratchet cam and drive gear have matching teeth on their facing
edges that mesh to turn them together in one direction only. When
the kick starter is not in use, a ramp on the cam is trapped behind the
stop bolt.
18. This ramp pulls the ratchet away from the driving gear so they
can't engage. When the kick starter lever is depressed, the ramp
on the ratchet moves from behind the stop bolt.
19. The ratchet moves to the left to engage the driving gear, which
turns with the movement of the kick starter lever. The gear is meshed
with a gear on the transmission main shaft. The main shaft rotates,
turning the clutch, primary drive, and crankshaft.
20. When the engine starts, the driving gear cannot turn the ratchet.
When the kick starter lever is released, the return spring moves the shaft
and ratchet back to their disengaged position.
21. The driving gear remains engaged to the mainshaft gear and turns
freely on the kickstarter shaft while the engine is running.
[previous page] [index]
[next page]

